Introduction
It’s nothing new to know about the attacks of the major and common ones’, but the new technique these attackers use to carry out their clandestine activities might shock you for a while. Malicious practices are carried out by phishing, vishing, probably via social engineering, baiting, trojan, etc. Lately, campaigns of malware have been carried out. This huge malware campaign has generated a malicious botnet (“a network robot). A botnet is a network of computers infected with malware ruled by a single attacking party.
The remains of how this malware has affected the proxies and how could it infect a bundle of working systems, right?
What are Proxy Servers and how does it work?
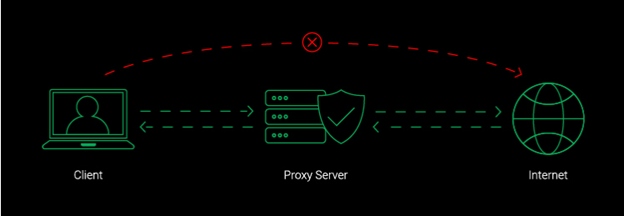
Proxy Servers are nothing more than intermediary systems or routers between the end user and the internet. Proxy servers have their own IP address they have the ability to prevent the attacks from entering into the network. Since proxy servers have their own IP address, act as a middleman or negotiator between your system and the internet. If you are searching for something on the internet, your system knows the address you are looking for, so it sends a request to the internet. It goes to the proxy server first, which gets acknowledged by the web servers and proceeds your searched data to your browser extension such as Chrome, Safari, Duck Duck Go, Brave, etc. This Proxy Server functions as a firewall or a data filter for your network.
Proxy Malware Campaigns and the Spread of it
In recent times, articles getting published about how malware is designed in a way that successfully skips the security layer in antivirus software also cripples the notifications and alerts seeking the user’s permission to install the application or not. The proxies are being delivered by a fleet of various other malware, which is probably spreading via looking for cracked versions of popular software, video games, lite applications, etc. Once the attacker gains control over the system, it executes certain files on that vulnerable system. Then the malware efficiently proceeds via downloading certain things on it and implementing proxy applications. This whole process takes place without intervention or seeking any permission from the user. In cases of the addition of installing adware, trojans take place and start to implement without the user’s knowledge.
The Configuration of these files
The configuration installer has two binaries,
- The foremost binary is used to establish communication with proxy commands and to control the IT infrastructure.
- For the installation of upgraded proxy applications.
The Resilience is maintained by a configuration key and a scheduled update task for the Windows Os systems. The proxy itself collects a large chunk of unique data from the host machine, which also includes the surveillance CPU storage, what processes are running, etc.
The question arises who is signing and bypassing the virus detection software?
Obviously, the attackers !! The attackers find out various ways to bypass virus detection using various methods. Here are a few ways it can happen:
- Unlawful Certificates: Attackers manage to secure illegitimate or stolen digital certificates that appear to be safe and valid to security software.
- Certificate Withdrawal Latency: Later on, when the certificates are found which are endangered, the process of withdrawing those certificates and upgrading the databases will take time and an advancement to the attacker too. During this window, malware signed with the undermined certificates would still be considered as legitimate by security software.
- Polymorphic malware: Some malware has a tendency to change its code time ever since its installation, generating new unique versions of itself.
- Legal Tools Abuse: Attackers might use lawful system administration and penetration testing tools to carry out malicious actions. In fact, these tools are known and trusted tools by the security software; the malware can be operated without any suspicion.
Conclusion :
In the world of cyber threats, a startling evolution is at play – a surge in sophisticated malware campaigns. These attacks manipulate our digital trust through tactics like phishing and trojans, paving the way for malicious botnets. These networks of compromised computers follow the command of a single attacker, orchestrating covert actions. Notably, these attacks cleverly exploit proxy servers, the intermediaries between users and the internet. Masked by digital signatures, these malware instances navigate antivirus defences, while deception bypasses user consent prompts. Moreover, these harmful proxies spread through seemingly innocent downloads, striking users seeking pirated software. Heightening concern, the malware’s stealthy configuration and polymorphic behaviour make detection an uphill battle. The question of who signs these malicious codes is? The attackers themselves, capitalising on stolen certificates, latency in certificate withdrawal, and the chameleon-like nature of polymorphic malware. This worrisome landscape underscores the dire need for heightened awareness and robust cybersecurity measures.
Reference:
Author: Sakshi Ankush Dhanawade Intern, Policy and Advocacy